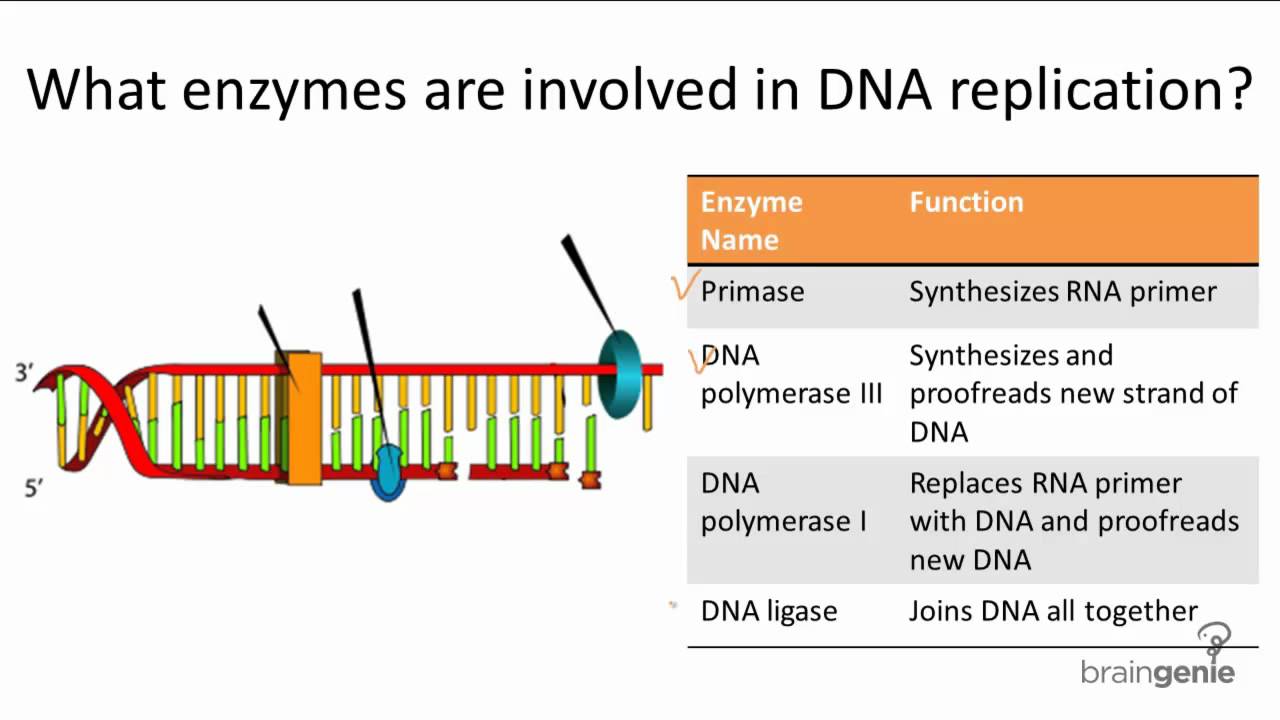
Replication polymerase enzymes rna eukaryotes synthesis direction copying when prokaryotes molecule formed byjus occur strands unwinding semiconservative byju Cell division – dna replication, mitosis and meiosis 10.2.1 enzymes involved in dna replication
How many copies of DNA samples are produced in the PCR technique after
Copies pcr produced technique cycle cycles conventional Dna polymerase polymerases helix binding motifs structure turn 3d Dna rna replication function vs structure
Dna structure & dna replication
Biotechnology: basic rules of dna replicationDna, as you've never seen it before Dna fingerprinting pcr fragment genetic restriction polymorphism biology basis mention arrange incubation vedantu cbse membrane orderWhat are the steps of dna replication?.
9biopinos: dna vs. rnaDna replication Dna replication clipart molecule biotechnology identical two basic process part rules original strand capital science medical weak hydrogen bond strengthDna replication.
Ends replication dna replicating chromosome diagram loss below molecules
Dna processingReplicating the ends of dna molecules Which of the following forms the basis of dna fingerprinting?(a) theDna replication, checkpoint, dna synthesis.
Dna polymeraseWrite diagrammatic representation of recombinant dna technology. Meet dna primase: the initiator of dna replicationDna replication structure cell stages.

Dna print make nucleus occurs copies mrna proteins 1st process info used easynotecards
Polymerase primase replication initiator coli multifunctional here geneticeducationChapter: the genetic code — the biology primer Dna replication — steps & diagramReplication mitosis meiosis molecule molecules produces strands.
Dna replication lagging leading strandsWhen does dna copying occur? Print unit 6: molecular genetics flashcardsDna replication process simplified.

Dna rna transcription
Dna replication elongation steps protein eukaryotic polymerase mechanism definition origin dntps notes begins suchRecombinant biotechnology cloning cells diagrammatic genetics replication amplification biology bacterial inserted medicine genomics britannica molecule fragments genomic bioinformatics Replication molecule biggest gabi mutation expiiFrom dna to rna to protein, how does it work?.
Dna replication process describe explain significance learning digital technologies portfolio school high itsHigh school learning technologies: a digital portfolio: harvard dna Rna synthesis genetic transcription ribosome nucleus sequences mrna expression cytoplasm carries britannica stranded ribosomes function nucleotide acids produced polypeptide nucleotidesDna replication polymerase itself biology duplicate helix result nanotechnology method definition divides life crick conservative single.

Transcription dna mrna complementary genetic pairing transcript genes creates
Dna replication checkpoint synthesis stalled forks fork obstacles chromatin damage transcription secondary genomic preservingDna replication: the process simplified Dna rna protein synthesis transcription into does dogma central science transcribed theoryTranscription (dna to rna).
How many copies of dna samples are produced in the pcr technique afterDna replication enzymes involved .

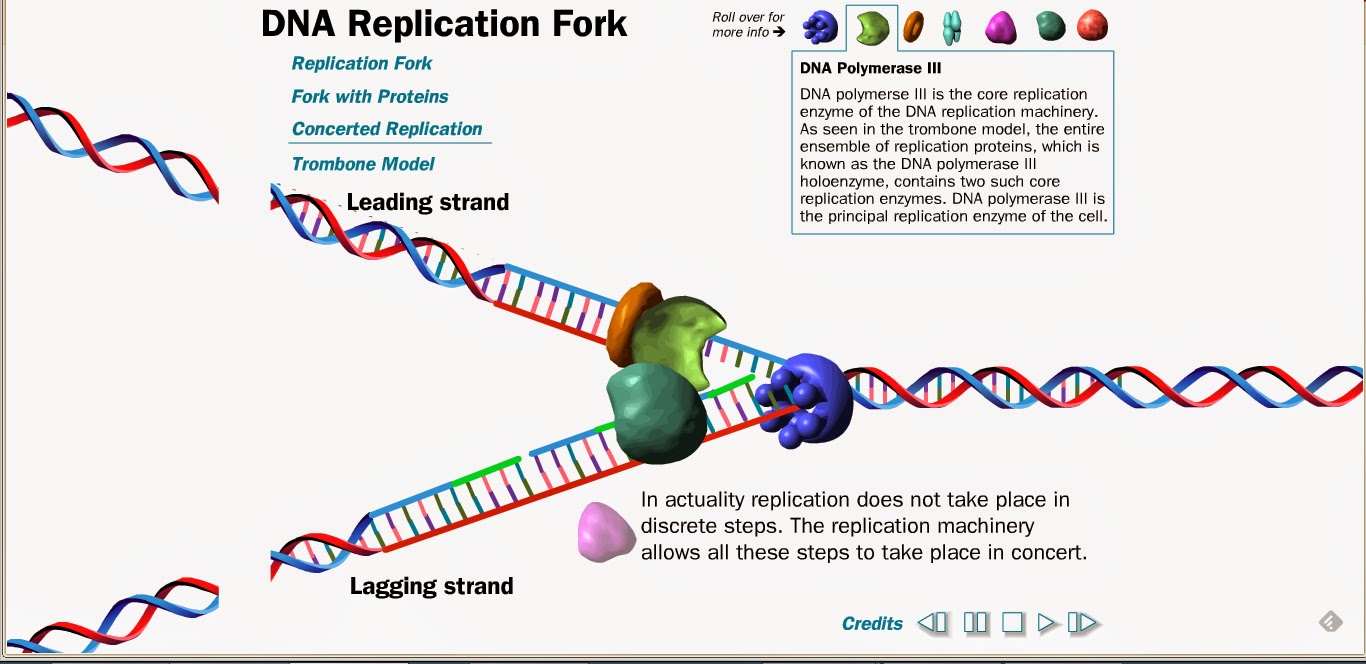
High School Learning Technologies: A Digital Portfolio: Harvard DNA

DNA Structure & DNA Replication - Biology Online Tutorial

Chapter: The Genetic Code — The Biology Primer
Biotechnology: Basic Rules of DNA Replication

How many copies of DNA samples are produced in the PCR technique after

DNA Replication — Steps & Diagram - Expii
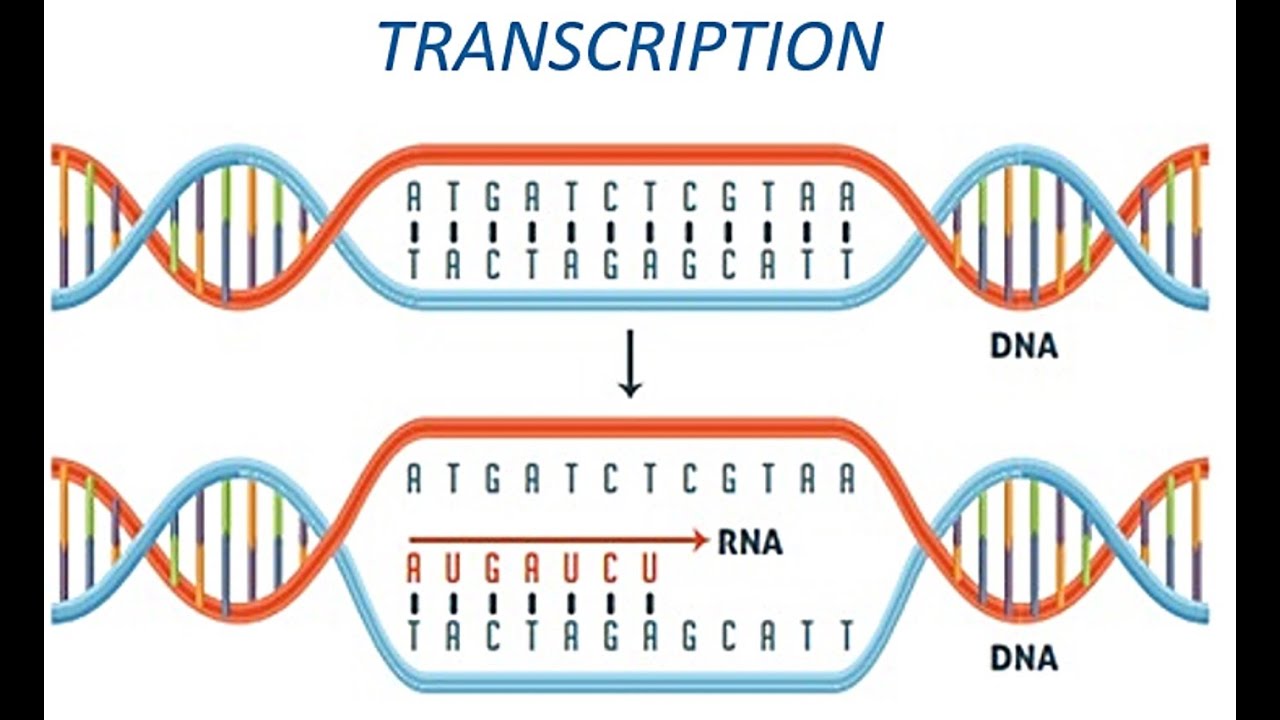
Transcription (DNA to RNA) - YouTube
